RAG: Retrieval Augmented Generation¶
Nixiesearch supports RAG-style question answering over fully local LLMs. For improved document retrieval quality in RAG pipelines, consider using cross-encoder reranking to ensure the most relevant documents are passed to the LLM.
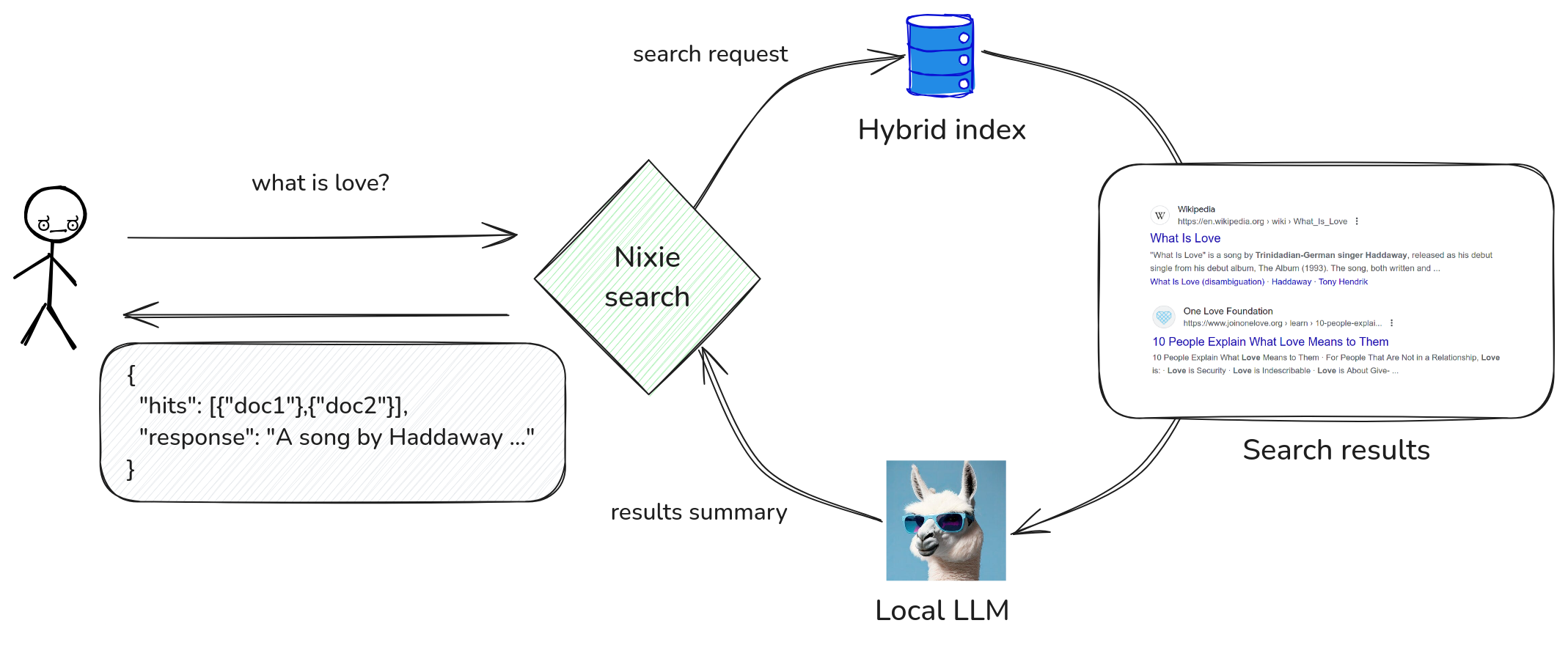
To use RAG queries, you need to explicitly define in the inference section of the config file which LLMs you plan to use query-time:
inference:
embedding:
# Used for semantic retrieval
e5-small:
model: intfloat/e5-small-v2
completion:
# Used for summarization
qwen2:
provider: llamacpp
# Warning: this is a very small and dummy model
# for production uses consider using something bigger.
model: Qwen/Qwen2-0.5B-Instruct-GGUF
file: qwen2-0_5b-instruct-q4_0.gguf
schema:
movies:
fields:
title:
type: text
search:
semantic:
model: e5-small
overview:
type: text
search:
semantic:
model: e5-small
Where:
model: a Huggingface model handle in a format ofnamespace/model-name.name: name of this model you will reference in RAG search requests
Nixiesearch uses a default prompt format from the GGUF model.
Sending requests¶
For RAG requests, Nixiesearch supports REST and Server Side Events for streaming responses:
- REST: much simpler to implement, but blocks till full RAG response is generated.
- SSE: can stream each generated response token, but is more complex to set up.
Request format is the same for both protocols:
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"fields": ["title", "description"],
"query": "what is pizza"
}
},
"fields": ["title", "description"],
"rag": {
"prompt": "Summarize search results for a query 'what is pizza'",
"model": "qwen2",
"stream": false
}
}
The rag field has the following options:
stream(boolean, optional, defaultfalse): Should we stream response with SSE, or just block until the complete response is generated.prompt(string, required): A main instruction for the LLM.model(string, required): Model name from therag.modelsindex mapping section.fields(string[], optional): A list of fields from the search results documents to embed to the LLM prompt. By default, use all stored fields from the response.topDocs(int, optional): How many top-N documents to embed to the prompt. By default pick top-10, more documents - longer the context - higher the latency.maxDocLength(int, optional): Limit each document in prompt by first N tokens. By default, use first 128 tokens.maxResponseLength(int, optional): Maximum number of tokens LLM can generate. Default 64.
REST responses¶
A complete text of the LLM response you can find in a response field:
$> cat rag.json
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"fields": ["title"],
"query": "matrix"
}
},
"fields": ["title"],
"rag": {
"prompt": "Summarize search results for a query 'matrix'",
"model": "qwen2"
}
}
$> curl -v -XPOST -d @rag.json http://localhost:8080/movies/_search
{
"took": 3,
"hits": [
{
"_id": "604",
"title": "The Matrix Reloaded",
"_score": 0.016666668
},
{
"_id": "605",
"title": "The Matrix Revolutions",
"_score": 0.016393442
},
],
"aggs": {},
"response": "The following is a list of search results for the query 'matrix'. It includes the following:\n\n- The matrix is the first film in the \"Matrix\" franchise."
}
Streaming responses¶
The main REST search endpoint /<index_name>/_search can also function as an SSE endpoint.
$> cat rag.json
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"fields": ["title"],
"query": "matrix"
}
},
"fields": ["title"],
"rag": {
"prompt": "Summarize search results for a query 'matrix'",
"model": "qwen2",
"stream" true
}
}
$> curl -v -XPOST -d @rag.json http://localhost:8080/movies/_search
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Date: Fri, 13 Sep 2024 16:29:11 GMT
< Connection: keep-alive
< Content-Type: text/event-stream
< Transfer-Encoding: chunked
<
event: results
data: {"took":3,"hits":["... skipped ..."],"aggs":{},"ts":1726246416275}
event: rag
data: {"token":"Summary","ts":1726246417457,"took":1178,"last":false}
event: rag
data: {"token":":","ts":1726246417469,"took":12,"last":false}
event: rag
data: {"token":" Searches","ts":1726246417494,"took":24,"last":false}
event: rag
data: {"token":" for","ts":1726246417511,"took":18,"last":false}
event: rag
data: {"token":" '","ts":1726246417526,"took":15,"last":false}
event: rag
data: {"token":"matrix","ts":1726246417543,"took":17,"last":true}
SSE response consists of two frame types:
results: a regular search response as for non-streaming requestsrag: a sequence of live generated per-token events.
results frame¶
A results frame has the following structure:
{
"took": 112,
"hits": [
{
"_id": "604",
"title": "The Matrix Reloaded",
"_score": 0.016666668
},
{
"_id": "605",
"title": "The Matrix Revolutions",
"_score": 0.016393442
}
],
"ts":1722354191905
}
Note
Note that unlike in the REST response, the results.response field is missing from the response payload: it is going to be streamed per token with the rag frames!
rag frame¶
A rag frame is a tiny frame always following the results frame:
{
"token": " Matrix",
"ts": 1722354192184,
"took": 20,
"last": false
}
token(required, string): next generated LLM tokents(required, long): generation timestamptook(required, long): how many millis underlying LLM spend generating this tokenlast(required, bool): is this the last token in the response stream?
Assembling frames together¶
- The
resultsframe with search results is always the first one - If there was a
request.ragfield present in the search request, server will start streaming RAG response tokens - When server finishes generating RAG response, it will set
last: trueflag to communicate that.